Technical 3d Animation for Industrial: technical 3d animation for industrial
Technical 3D animation for industrial applications breathes life into flat CAD models. It turns static designs into interactive visuals that untangle complex assemblies.
By adding motion and clarity, teams speed up decision-making and trainers sharpen skills without risking downtime or extra costs.
Seeing Blueprints Come Alive With 3D Animation
Picture a static engineering drawing morphing into a living, breathing prototype—gears rotate, conveyors hum, and you can study each movement from every angle.
This blueprint come alive analogy shows how 3D animation adds depth and motion to traditional CAD views, transforming dry schematics into intuitive, engaging stories.
- Manufacturers use technical 3D animation to visualise assembly sequences and spot fit issues before any metal is cut.
- Trainers recreate machine operations in a safe virtual setting, cutting training time and reducing risk.
- Engineers review dynamic renderings to verify fluid flow and structural integrity ahead of fabrication.
- Marketing teams produce explainer videos that demystify complex processes for wider audiences.
- Sales departments offer interactive demos to engage prospects and shorten the sales cycle.
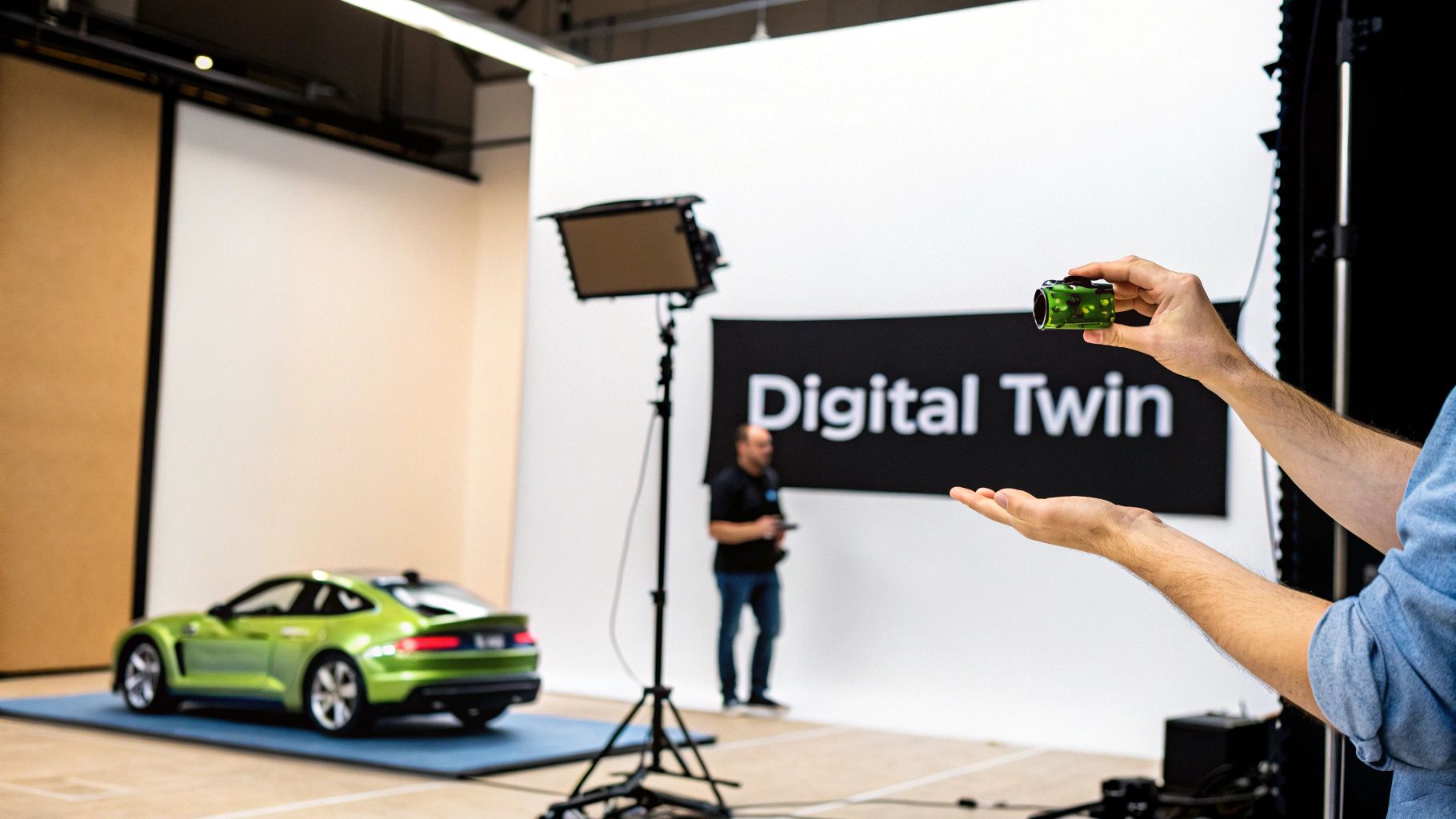
Technical animations act like digital twins, mirroring real-world machinery with pixel-perfect accuracy.
Why Poland Market Matters
Between 2024 and 2032, the Poland animation market is poised to climb from USD 2,736.33 billion to roughly USD 3,564.86 billion, driven by growing demand for 3D/CGI content and international outsourcing. See the full market projections in the Poland Animation Market Report.
As we journey through this guide, you’ll move from foundational concepts to hands-on production steps and essential technical checklists. Don’t miss our Voestalpine 3D animation showcase to see these ideas in action: Learn more about the Voestalpine showcase.
What You Will Learn
- Key Principles and terminology to navigate technical 3D workflows
- A Step-by-Step Overview of the production pipeline, from CAD import to final VFX
- Insights into File Formats, simulation tools and accuracy considerations
- Typical Deliverables, cost drivers and timeline phases for industrial projects
- Criteria for Choosing the Right 3D Animation Studio based on your specific needs
Let’s dive into the core concepts and discover how 3D animation can revolutionise your industrial visuals.
Understanding Technical 3D Animation Concepts
Technical 3D animation for industrial projects is all about precision, interactivity and scale. Picture a digital twin as a tangible prototype you can turn over in your hands. It’s where raw CAD data transforms into a detailed, accurate visual narrative through three core stages.

Three Core Processes
- Geometry Modelling refines engineering CAD into 3D meshes accurate to the nearest metre.
- Material Shading layers on textures and lighting that mirror real-world surface properties.
- Motion Scripting choreographs part movements so kinematics and timing adhere to the original specifications.
Building Interactive Models
When geometry modelling, material shading and motion scripting unite, you get a fully interactive digital twin. Users can pan, zoom and probe each part in real time. It’s like inspecting a machine without ever taking it apart.
- Rotate and zoom for clear spatial orientation.
- Isolate components to focus on specific details.
- Run scenario simulations to uncover potential failure modes.
These tools let engineers spot design flaws long before the first prototype is built. For instance, animating fluid flow inside a valve reveals hidden behaviours, while visualising heat exchange in a sink makes thermal dynamics crystal clear.
Distinguishing Industrial Animation
Unlike entertainment CGI, industrial animation hinges on exacting detail at every step. Every millimetre and time increment must match real-world specifications. This rigor supports training programmes, maintenance planning and safety analyses.
Key Insight: A digital twin acts like a virtual replica that mirrors real machinery with pixel-perfect accuracy.
Integrating CAD Metadata
Everything starts with CAD files packed with metadata on tolerances and assembly relationships. Preserving unit settings and coordinate systems is vital to avoid scale errors on import.
- Tolerance Values set precise fitting clearances.
- Part Numbers and hierarchies keep complex assemblies organised.
- Material IDs tie components to the correct shading presets.
By keeping these data points intact, each part behaves and appears exactly as the engineers intended. At its core, a digital twin is an interactive model where scenarios can be tested safely.
Independent Poland market studies estimate Poland’s 3D/motion design market at roughly USD 20.5 billion in 2025 with projections to reach USD ~52.0 billion by 2033. Learn more in the Poland market report.
Understanding these layers of data integration and interactive features demonstrates why technical 3D animation for industrial projects demands rigorous planning. These foundational concepts pave the way for a closer look at the production pipeline in the next section.
Production Pipeline From CAD To Rendering And VFX
Our pipeline works much like a manufacturing line. Each stage refines raw CAD data into detailed, production-ready visuals.
It starts with CAD Import, where STEP and IGES files are brought in, errors are spotted and parts are organised. Early cleanup prevents scale headaches and broken meshes down the road.
Production Pipeline Stages Comparison
Before we press on, here’s a snapshot of each key phase:
| Stage | Input | Tools | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAD Import | STEP and IGES files | CAD software | Cleaned geometry |
| Asset Polishing | Meshes and textures | Modelling tools | Production-ready assets |
| Rigging | Geometry and joints | Rigging systems | Animated part assemblies |
| Simulation | Rigid bodies and fluids | Physics engines | Realistic motion sequences |
| Rendering and VFX | Scenes and lighting | Renderers and compositors | Final frames and effects |
Each column highlights how data transforms—from raw CAD to those polished frames you see on screen.
Key Rigging And Assembly Steps
Rigging is where static geometry learns to move. Typical tasks include:
- Defining joint hierarchies and precise pivot points.
- Applying mechanical constraints to simulate stops or limits.
- Labelling controls clearly for greater animator speed.
Simulation For Real-World Motion
Simulation injects forces and interactions into your scene:
- Use rigid-body solvers to handle collisions between parts.
- Deploy fluid engines for realistic liquid or gas behaviour.
- Tweak collision margins to avoid unwanted mesh intersections.
Rendering And Visual Effects Best Practices
This final stage brings everything to life with light and effects:
- Adjust sample rates and output resolution to match deliverable specs.
- Apply denoising and layered compositing for cleaner frames.
- Optimise light bounces to keep render times in check.
- Export separate passes (diffuse, specular, Z-depth) for flexible post-work.
Integration Tools And Software
A handful of platforms tie this whole process together:
- Autodesk Maya excels at rigging and keyframe animation.
- SideFX Houdini is the go-to for procedural VFX and simulation.
- Blender offers open-source flexibility plus a huge plugin library.
- Autodesk 3ds Max handles engineering file formats with ease.
Custom Python or MEL scripts can automate repetitive tasks. And tools like Git or Perforce track every asset revision.
Take a look at our detailed animation production pipeline guide for deeper insights into each phase.
Final Quality Checks
A solid QA routine ensures nothing slips through:
- Run material consistency audits to catch incorrect textures.
- Conduct playback tests to verify smooth loops.
- Review render previews for proper lighting and framing.
Building buffer time for feedback rounds keeps both timelines and budgets on track.
Maintain clear sequencing at every hand-off—this is the backbone of any successful technical animation project.
Technical Requirements For Industrial Animation Projects
Getting the technical foundations right is half the battle when you’re working on complex industrial visuals. You need the best file formats to preserve every curve and corner. At the same time, you’re juggling polygon budgets to keep render times in check and deadlines on track.
On the data-management side, version control and security protocols are non-negotiable. Teams commonly lean on platforms like Perforce or Git, paired with cloud storage, to make sure every model update is logged and audited.
Below is an infographic illustrating the CAD to render pipeline from import through rigging to final frames.
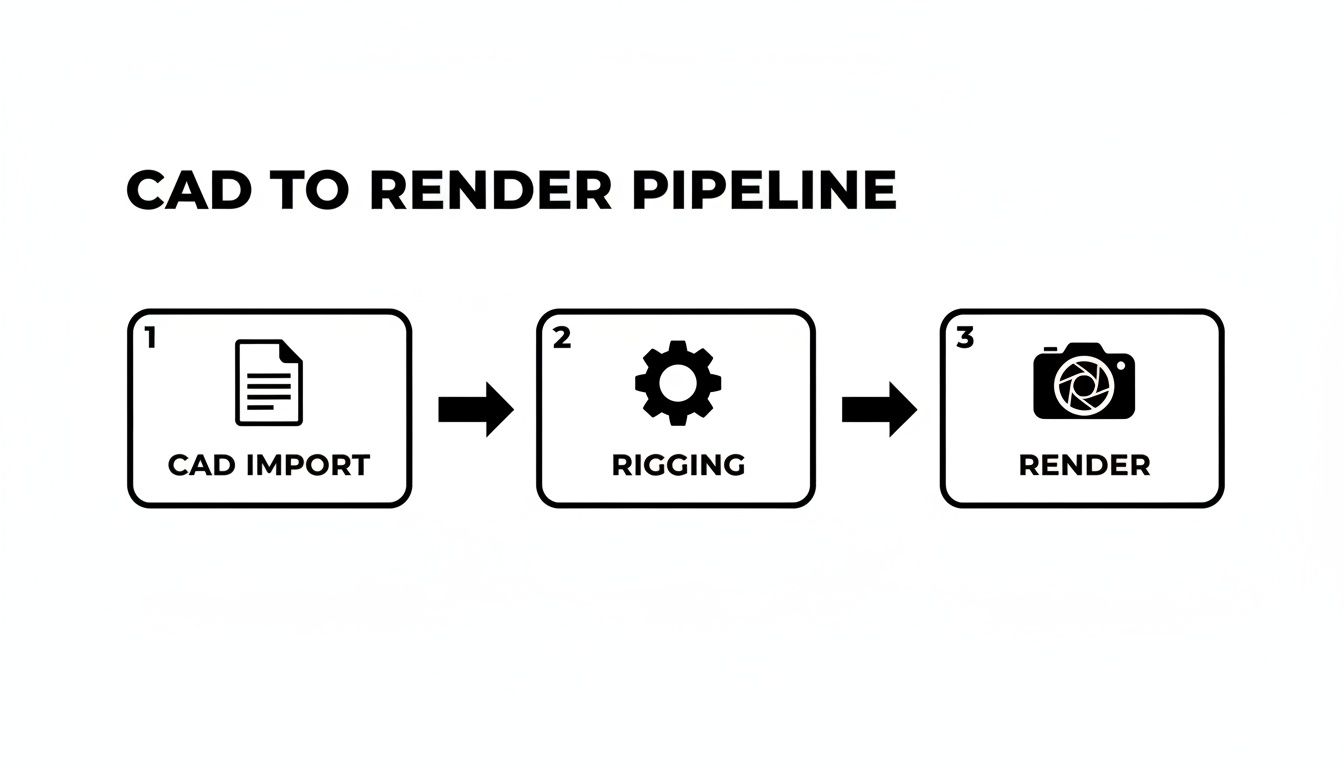
It shows how clean CAD data transforms into animation rigs and, ultimately, polished frames without wasted effort.
Looking at the vendor landscape, Poland has become a hotspot for specialised 3D animation and VFX studios. As of late 2025, client rates sit between USD 50–149, and mid-sized houses report 3D animation making up 30–90% of their offerings. Discover more insights about Poland’s 3D vendor landscape on clutch.co.
Choose Suitable File Formats
- STEP files retain exact boundary representation and full solid-geometry detail.
- IGES works well for legacy data exchange but often needs cleanup after import.
- FBX carries animation metadata and camera moves, making it perfect for downstream pipelines.
- glTF offers web-friendly delivery, compact file sizes and PBR compatibility.
Balancing polygon counts might mean using mesh decimation or LOD workflows. This approach keeps frame rates smooth during interactive reviews or VR demos.
Balance Performance And Quality
Your choice of simulation engine should reflect project goals. Fluid-dynamics modules shine with pouring liquids, while rigid-body solvers excel at mechanical kinematics. Fine-tune collision margins and substep rates to eliminate jitter without sending compute times through the roof.
Deliverables must match client expectations: MP4 provides quick, compressed previews, whereas EXR sequences deliver frame-by-frame data for compositing. And don’t forget: secure transfers via FTP or SFTP protect your IP when handing off assets.
Learn more about technical video production workflows in our detailed guide at Simple Frame.
Expert Insight: Schedule regular technical reviews at each deliverable milestone to catch issues early.
Maintain Asset Version History
- Use clear, descriptive commit messages for every model revision.
- Label branches by discipline or date so reviews stay organised.
- Archive deprecated assets in a dedicated folder to prevent accidental reuse.
Standardising naming conventions across design, engineering and animation assets removes confusion and speeds up handoffs. Preserving dimensional precision and optimising workflows ensures your industrial animations meet engineering standards while remaining efficient.
Deliverables And Major Cost Drivers
Every industrial 3D animation project revolves around clearly defined outputs. Whether you’re showcasing an Animated Walkthrough or delivering a Digital Twin, each deliverable fulfils a unique role—be it training, design validation or marketing outreach. Choosing the right file type—MP4, MOV, glTF or a Unity package—keeps client platforms happy and interactions seamless.
Picking formats early strikes the balance between file size, visual fidelity and smooth playback. Nail these decisions at the outset and you’ll sidestep compatibility headaches down the road.
Deliverables And Formats Summary
Below is a quick overview of the most common deliverables, their go-to formats and where they shine in practice.
| Deliverable | Format | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Animated Walkthrough | MP4 / MOV | Client presentations and sales pitches |
| Exploded-View Sequence | MP4 / EXR sequence | Engineering reviews and documentation |
| Interactive VR Demo | Unity package / glTF | Immersive training and virtual prototyping |
| Digital Twin | glTF / custom engine build | Ongoing asset updates and maintenance |
This table helps you match project goals to formats, smoothing out delivery and playback across platforms.
Timeline Phases And Cost Drivers
A typical project breaks down into three phases: pre-production, production and post-production. Each stage brings its own budget considerations, so understanding these cost drivers upfront prevents unwelcome surprises.
Key factors include:
- Rig Complexity: More articulation means extra animator hours and scripting effort.
- Simulation Accuracy: High-fidelity physics or fluid sims can spike computation time.
- Rendering Resolution: Pushing DPI or frame rate raises render farm hours.
- Iteration Cycles: Every revision round adds both time and expense.
In one example, adding a fluid simulation doubled the simulation budget and extended the schedule by nearly two weeks.

This screenshot breaks down effort estimates versus scope items, showing how even small scope tweaks can shift your budget brackets.
Tips For Budget Planning
Getting deliverable specs locked in early slashes unnecessary back-and-forth and keeps costs in check.
Expert Insight
Detailed scope documents are your best defence against scope creep and unexpected expenses.
Best practices for realistic budgets:
- Define each deliverable and its format at kickoff.
- Estimate hours per revision cycle and add a healthy buffer.
- Align rendering specs (resolution, codec, frame rate) with client expectations from day one.
- Schedule regular budget reviews to catch overruns before they escalate.
A survey of 200 industrial 3D animation projects showed that clear deliverable specifications cut revision cycles by 35% and helped teams stay within budget 82% of the time. For deeper insights, see the official industrial animation deliverables study.
Clear budgets and realistic timelines drive smoother delivery and happier clients.
Choosing The Right 3D Animation Studio
Picking a 3D animation partner is a lot like choosing a steering engine for a ship—it sets the course for your entire voyage. Focusing solely on price is tempting, but it’s only one piece of the puzzle.
Begin by scanning portfolios for projects that echo your industry and scale. Pay attention to assemblies, materials and simulation challenges they’ve tackled before.
Check for recognised certifications—think ISO standards or engineering alliance badges—and make sure their toolchain speaks your CAD’s language (STEP, FBX or glTF).
Ask about their communication rhythm. Clear feedback loops and milestone reviews keep everyone rowing in sync.
- Review past industrial animations with comparable complexity and scale.
- Request a full breakdown of software tools and pipeline stages.
- Confirm secure data exchange methods for CAD models and assets.
- Inquire about internal review gates and preview schedules.
- See if their core team includes mechanical or process engineers.
Vendor Evaluation Checklist
Use these questions to shave your shortlist down to the best contenders:
- What engineering disciplines form the core team, and what qualifications back them?
- How do they safeguard your confidential data and intellectual property?
- Can they provide a transparent, phase-by-phase cost estimate?
- How do they manage technical revisions once the first cut is delivered?
- Do they offer post-delivery support or hands-on training for your team?
Red flags appear when studios skip engineering sign-off or offer one-way approval loops.
Green flags shine through clear cost breakdowns and timely previews for feedback.
Expert Tip Ask for a detailed cost breakdown at kick-off to avoid any budget surprises later.
With this simple framework, you’ll quickly see which studios blend engineering precision with creative flair. Next, request sample schedules to align on timelines and budget phases.
Next Steps For Vendor Selection
Finalise your shortlist by scoring each studio against the above criteria. Then:
- Host a kickoff workshop to introduce teams and agree communication norms.
- Confirm toolchain setups and data-transfer protocols—no last-minute hiccups.
- Document all milestones and deliverable formats to keep everyone on the same page.
This structured approach ensures your industrial 3D animation project stays on track, on budget and up to your technical standards.
Learn more about evaluating technical animation partners in our engineering and technical animation guide for deeper guidance.
Case Studies And Next Steps
Nothing illustrates the power of technical 3D animation quite like seeing it in action. Below are three industrial success stories—each one revealing goals, obstacles and hard numbers.
Manufacturing Line Simulation
A global manufacturer wrestled with dry, static diagrams that left new hires guessing at conveyor timing and sensor triggers. To bring clarity, we crafted a 3D sequence showing every belt speed and activation point.
- Project Goal: Visualise a complex assembly line and slash training time
- Technical Hurdle: Integrate CAD data from five separate machine modules
- Applied Solution: Custom Python scripts automated geometry import and synced animations
The payoff? A 40% reduction in hands-on training hours and zero errors during practical assessments.
Medical-Device Assembly Demo
Designers of a precision medical device faced a nearly 15% misalignment rate when relying on flat, printed guides. By presenting an exploded-view 3D video that walked operators through each screw torque and part orientation, they saw immediate gains:
Key Insight: Animating each assembly step sharpens operator accuracy and standardises procedures.
- Accuracy Increase: 30% fewer assembly errors
- Inspection Time: Manual reviews cut by half
Digital Twin For Petrochemical Plants
A refinery upgrade request hinged on stakeholder confidence for a $2.4 billion investment. We built a real-time digital twin, simulating fluid flows and pressure shifts with a physics engine and layered VFX. Results in stakeholder engagement speak for themselves:
| Metric | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Stakeholder Buy-In | 60% | 90% |
| Approval Cycle Time | 5 days | 2 days |
This immersive model accelerated approvals and drove down budget uncertainty.
Next Steps Checklist
- Define a small-scale proof-of-concept using key components
- Gather early feedback from engineers and operators
- Refine animations for both accuracy and visual clarity
- Scale up once initial objectives are achieved
Ready To Launch
Use this checklist to steer your first project. Partner with a studio that marries engineering precision with compelling visual storytelling. Track milestones and review early renders to keep every detail on target.
Frequently Asked Questions
People often ask about the nuts and bolts of technical 3D animation in industrial settings. Below, you’ll find straightforward answers drawn from studio experience and typical project benchmarks. If you want more detail, hop back up to the relevant sections on methods and cost breakdowns.
Common Questions And Answers
- What budget should I allocate for a simple industrial animation?
For a basic walkthrough without heavy simulations, plan on USD 5,000 to USD 15,000. We also recommend setting aside a 15–20% revision buffer. - Which software is best for industrial fluid simulations?
In our projects, Autodesk CFD, Blender’s Mantaflow and SideFX Houdini top the list. Each has its own licensing needs and learning curve, so factor in your team’s skills and pipeline. - How long does an industrial 3D animation project usually take?
You should expect 4–12 weeks end-to-end:- Concept & CAD prep: 1–2 weeks
- Animation & simulations: 2–4 weeks
- Rendering & revisions: 1–4 weeks
- Can we use existing CAD models for animation?
Absolutely. Cleaning up geometry, setting up rigs and simplifying meshes will take roughly 20–30% of your prep time. A tidy import means fewer hiccups later and correct scale throughout the project.
A clean CAD import and crystal-clear deliverable specs are your best defence against scope creep and surprise costs.
Ready to see your ideas come alive with pinpoint accuracy? Get in touch with Simple Frame to discuss your next industrial 3D animation project.
